Definition - What does Oscillator mean?
An oscillator is an electronic or mechanical gadget that produces standard motions as electrical or mechanical vitality. Cutting edge PCs, timekeepers, metal identifiers, watches and microcontrollers all use oscillators. A nuclear clock works on nuclear motions, and in this manner is said to be the most exact chronometer on the planet. An oscillator takes a shot at the recurrence that is controlled by quartz gem.Techopedia clarifies Oscillator
Oscillators in gadgets are utilized in remote transmitters and collectors to produce and gather constant sign. They are likewise utilized in music synthesizers for tasks and controls of sound recurrence. Regardless of whether electronic or mechanical, all oscillators have one basic standard of activity: a delicate intensifier is utilized whose yield is nourished back to the info terminal, shaping a positive criticism circle framework. Along these lines the sign is recovered from its past state, consequently continuing itself. Different oscillators utilize combinational circuits with capacitors, inductors and resistors so as to accomplish a specific recurrence. Tickers related with microcontrollers and preparing units of PCs have a recurrence scope of megahertz (MHz).Electronic oscillator
 An electronic oscillator is an electronic circuit that delivers an intermittent, swaying electronicsign, regularly a sine wave or a square wave.[1][2][3] Oscillators convert direct current (DC) from a power supply to a rotating current (air conditioning) signal. They are generally utilized in many electronic gadgets ranging from least complex clock generators to advanced instruments (like adding machines) and complex PCs and peripherals etc.[3] Normal instances of sign created by oscillators incorporate sign communicate by radio and television transmitters, clock flag that direct PCs and quartz
An electronic oscillator is an electronic circuit that delivers an intermittent, swaying electronicsign, regularly a sine wave or a square wave.[1][2][3] Oscillators convert direct current (DC) from a power supply to a rotating current (air conditioning) signal. They are generally utilized in many electronic gadgets ranging from least complex clock generators to advanced instruments (like adding machines) and complex PCs and peripherals etc.[3] Normal instances of sign created by oscillators incorporate sign communicate by radio and television transmitters, clock flag that direct PCs and quartz timekeepers, and the sounds delivered by electronic beepers and video games.[1]
Oscillators are frequently portrayed by the recurrence of their yield signal:
A low-recurrence oscillator (LFO) is an electronic oscillator that produces a recurrence beneath roughly 20 Hz. This term is commonly utilized in the field of sound synthesizers, to distinguish it from a sound recurrence oscillator.
 A sound oscillator produces frequencies in the sound range, around 16 Hz to 20 kHz.[2]
A sound oscillator produces frequencies in the sound range, around 16 Hz to 20 kHz.[2]A RF oscillator produces flag in the radio recurrence (RF) range of around 100 kHz to 100 GHz.[2]
Oscillators intended to create a powerful air conditioning yield from a DC supply are normally called inverters.
There are two principle sorts of electronic oscillator – the direct or symphonious oscillator and the nonlinear or unwinding oscillator
Criticism oscillator
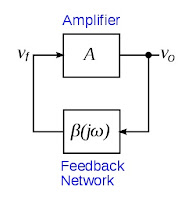
The most widely recognized type of straight oscillator is an electronic intensifier, for example, a transistor or operational enhancer associated in a criticism circle with its yield nourished go into its contribution through a recurrence particular electronic channel to give positive input. At the point when the power supply to the enhancer is first turned on, electronic noise in the circuit gives a non-zero sign to kick motions off. The noise goes around the circle and is enhanced and sifted until rapidly it meets on a sine wave at a solitary recurrence.
Input oscillator circuits can be characterized by the kind of recurrence particular channel they use in the criticism loop:[2][4]
In a RC oscillator circuit, the channel is a system of resistors and capacitors.[2][4] RC oscillators are for the most part used to produce lower frequencies, for instance in the sound range. Normal kinds of RC oscillator circuits are the stage move oscillator and the Wien connect oscillator.
In a LC oscillator circuit, the channel is a tuned circuit (regularly called a tank circuit; the tuned circuit is a resonator) consisting of an inductor (L) and capacitor (C) associated together.[2][4] Charge streams to and fro between the capacitor's plates through the inductor, so the tuned circuit can store electrical vitality swaying at its resonant recurrence. There are little misfortunes in the tank circuit, however the speaker makes up for those misfortunes and supplies the influence for the yield signal. LC oscillators are regularly utilized at radio frequencies,[2] when a tunable recurrence source is important, for example, in signal generators, tunable radio transmitters and the neighborhood oscillators in radio recipients. Commonplace LC oscillator circuits are the Hartley, Colpitts[2] and Clapp ccircuits.
Two regular LC oscillator circuits, the Hartley and Colpitts oscillators
In a precious stone oscillator circuit the channel is a piezoelectric gem (normally a quartz crystal).[2][4] The gem mechanically vibrates as a resonator, and its recurrence of vibration decides the swaying recurrence. Precious stones have an extremely high Q-factor and additionally preferable temperature dependability over tuned circuits, so gem oscillators have much preferred recurrence strength over LC or RC oscillators. Precious stone oscillators are the most widely recognized kind of straight oscillator, used to settle the recurrence of most radio transmitters, and to create the check signal in PCs and quartz timekeepers. Precious stone oscillators frequently utilize indistinguishable circuits from LC oscillators, with the gem supplanting the tuned circuit;[2] the Penetrate oscillator circuit is likewise generally utilized. Quartz gems are commonly restricted to frequencies of 30 MHz or below.[2] Different sorts of resonators, dielectric resonators and surface acoustic wave (SAW) gadgets, are utilized to control higher recurrence oscillators, up into the microwave range. For instance, SAW oscillators are utilized to create the radio sign in mobile phones.
Negative-resistance oscillator
Notwithstanding the criticism oscillators depicted above, which utilize two-port intensifying dynamic components, for example, transistors and operational speakers, direct oscillators can likewise be constructed utilizing one-port (two terminal) gadgets with negative resistance,[2][4], for example, magnetron tubes, burrow diodes, IMPATT diodes and Gunn diodes. Negative-resistance oscillators are typically utilized at high frequencies in the microwave range and above, since at these frequencies input oscillators perform ineffectively because of inordinate stage move in the criticism way.
In negative-resistance oscillators, a resonant circuit, for example, a LC circuit, precious stone, or hole resonator, is associated over a gadget with negative differential resistance, and a DC inclination voltage is applied to supply vitality. A resonant circuit without anyone else's input is "very nearly" an oscillator; it can store vitality as electronic motions whenever energized, but since it has electrical resistance and different misfortunes the motions are damped and rot to zero. The negative resistance of the dynamic gadget cancels the (positive) inside misfortune resistance in the resonator, in actuality making a resonator with no damping, which creates spontaneous ceaseless motions at its resonant recurrence.



0 Comments