What is a diode?
A diode is a semiconductor gadget that basically goes about as a single direction switch for current. It enables current to stream effectively one way, yet seriously limits current from streaming the other way.
Diodes are otherwise called rectifiers since they change exchanging current (air conditioning) into throbbing direct current (dc). Diodes are appraised by their sort, voltage, and current limit.
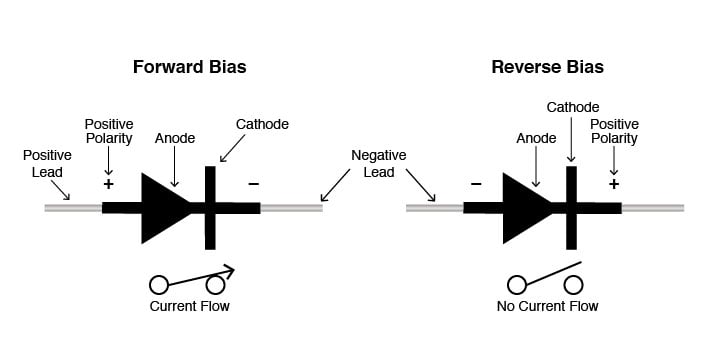
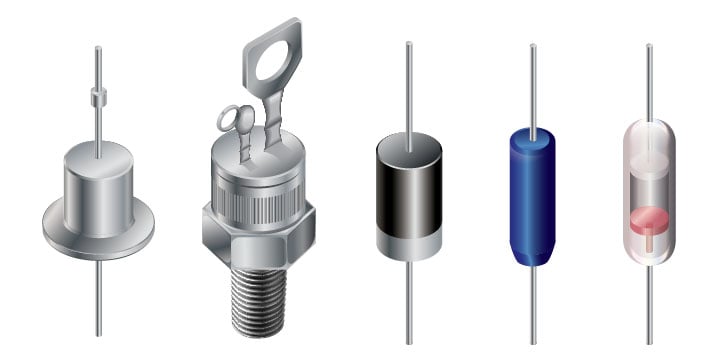
Diodes have extremity, controlled by an anode (positive lead) and cathode (negative lead). Most diodes enable current to stream just when positive voltage is applied to the anode. An assortment of diode setups are shown in this realistic:
Diodes are accessible in different setups. From left: metal case, stud mount, plastic case with band, plastic case with chamfer, glass case.
At the point when a diode permits current stream, it is forward-one-sided. At the point when a diode is turn around one-sided, it goes about as a protector and doesn't allow current to stream.
Weird yet obvious: The diode image's bolt focuses against the course of electron stream. Reason: Engineers considered the image, and their schematics show current spilling out of the positive (+) side of the voltage source to the negative (- ). It's a similar show utilized for semiconductor images that incorporate bolts—the bolt focuses the allowed way of "regular" stream, and against the allowed bearing of electron stream.
An advanced multimeter's diode test diode delivers a little voltage between the test drives enough to advance predisposition a diode intersection. Typical voltage drop is 0.5 V to 0.8 V. The forward-one-sided obstruction of a decent diode should extend from 1000 ohms to 10 ohms. At the point when invert one-sided, an advanced multimeter's showcase will peruse OL (which demonstrates high opposition).


0 Comments